A new study looks at trends in global wildfire frequency and damage costs.
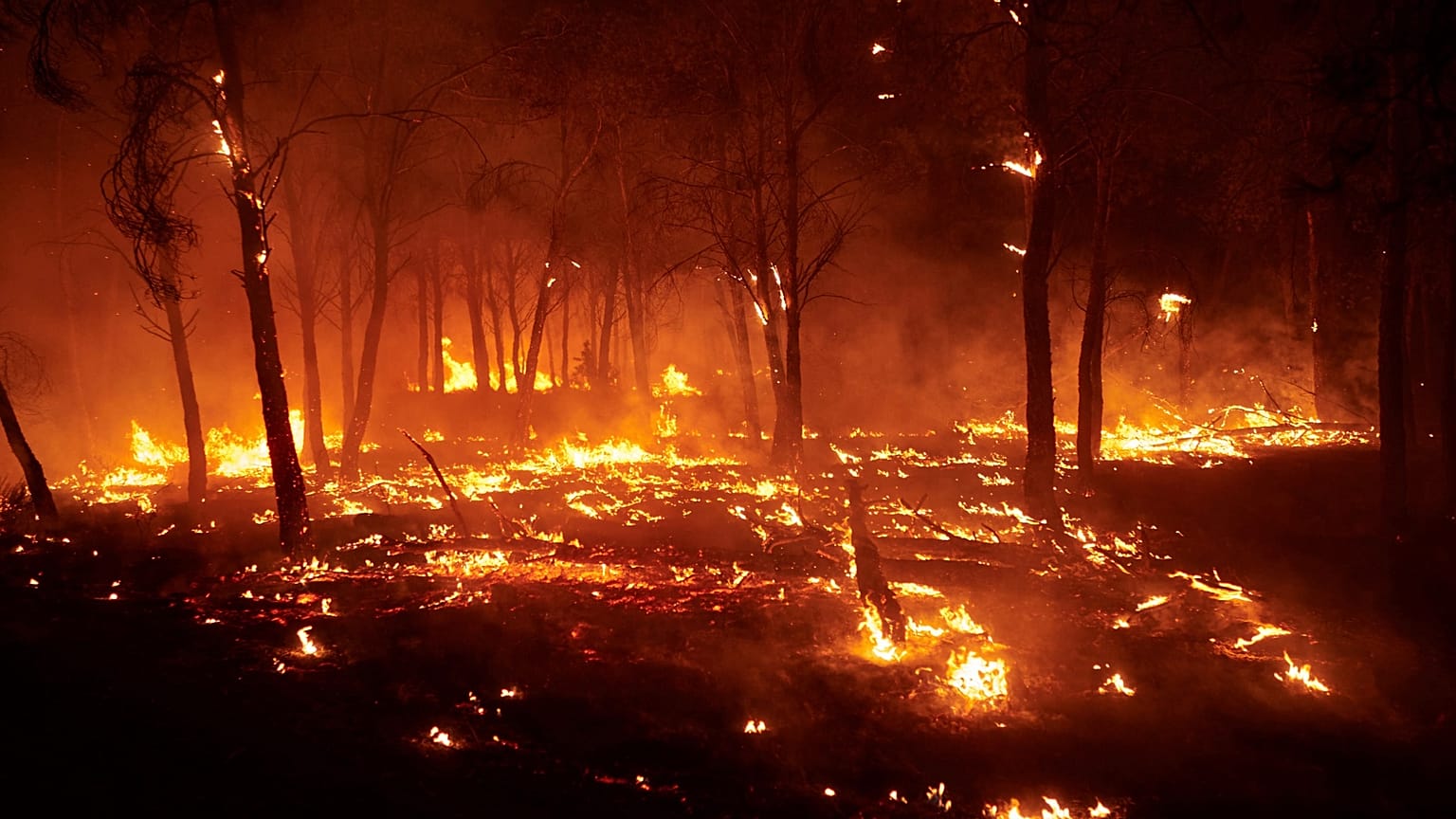
Wildfires are becoming more disastrous and costly, a new study reveals.
 ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
 ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Climate change makes natural environments more prone to wildfires. A new study, published in Science, shows how wildfires have become more frequent and disastrous in the past 44 years.
Fire is a natural process that is important for the health of ecosystems. But climate change, land mismanagement, and expansion into flammable landscapes have intensified fire risks. These wildfires are becoming more lethal and expensive.
Worsening fire seasons
This summer saw a record amount of fire destruction across the European continent. Not all countries are affected equally: Spain and Portugal have recorded the worst damage, with climate change fuelling wildfires of “unprecedented intensity”
This new study analysed global disaster databases spanning 1980 to 2023. They identified major wildfire disasters - those that caused 10 or more fatalities or were among the 200 largest wildfire-related economic losses relative to national GDP. Researchers observed distributions, trends, and conditions.
Their analysis revealed that globally, wildfires are becoming more frequent and costly over time. Nearly half of the most damaging events during the time span they looked at occurred in the past decade. This is likely attributable to increasingly extreme fire weather in vulnerable and densely populated areas.
How does Europe compare?
As with the global trend, wildfire events and damage costs increased substantially in Europe in the past decade.
Wildfire disasters also tended to be concentrated in certain areas. The study found that Mediterranean forests were among the more fire-prone biomes. Mediterranean biomes experienced 6.7 times more disasters than expected based on their population sizes.
While North America saw the largest increase in absolute damage costs across the time period, Europe also had its share of “billion-dollar events” - wildfires that caused over a billion USD in damage.
How can countries prepare?
This study highlights a need for fire adaptation, especially as wildfires begin to emerge in the margins of affluent urban areas.
The EU has promised to strengthen its firefighting capabilities, deploying teams in the most vulnerable regions. However, as Euronews reported in September, activists and scientists claim that governments are still failing to prioritise prevention.
The study authors highlight the importance of being proactive with fire management and managing fuels through targeted prescribed burning. They also emphasised the need for initiatives that focus on helping citizens affected by fires.
“Mitigation must also address strategies to reduce fatalities by increasing evacuation effectiveness, especially for socially vulnerable populations who are the most likely to be killed in wildfires, as well as designing fire structures and defensible spaces where people can ‘shelter in place,’” the authors write.