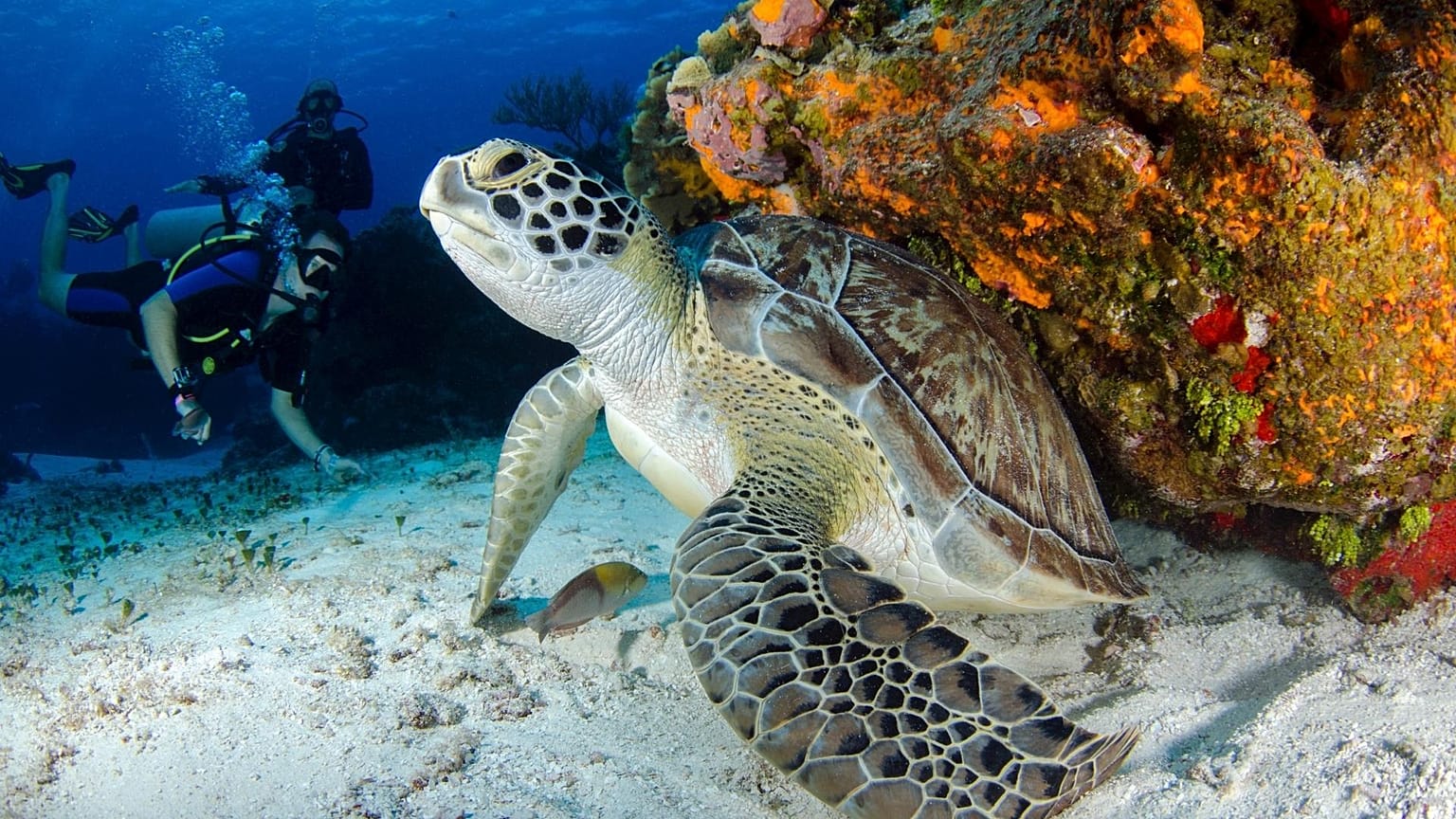
Rising temperatures in the Mediterranean Sea are attracting new species of fish, threatening local marine life.
Rising temperatures in the Mediterranean Sea are attracting new species of fish.
 ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
 ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Since the start of summer 2022, sea temperatures in the region have risen 5°C above average for this time of year. Successive heatwaves raging in France underpin this phenomenon.
Holidaymakers and divers in Hyères, Southern France, are enjoying the 27°C waters and unusual sightings of tropical species like barracuda, ornate wrasse, triggerfish and turtles - usually found in the Red Sea in Egypt.
According to diving instructor Mickael Youssouf, he has never seen more fish in this region in his 20 year career.
“For us as professionals, it’s great for all our clients, but in the long term, I think it will have environmental consequences,” he says.
How will rising sea temperatures impact marine life?
Though divers are enjoying the new visitors, the rising temperatures are not good news. The spectacle is likely to have a devastating effect on the marine ecosystem.
Experts fear the arrival of invasive exotic species, which could threaten food supplies and prey on native marine life. Invasive algae, meanwhile, could suffocate local corals and reduce water oxygenation.
“These species could be insatiable herbivores, or carnivores too, which will devour a lot of fish. They could also be invasive algae that will completely change our ecosystem," says Sandrine Ruitton, a teacher and researcher at the Mediterranean Institute of Oceanography.
Species that can migrate are likely to move to cooler habitats, while those that are left may struggle to survive.
How do invasive species reach the Mediterranean Sea?
Non-native species of fish get introduced to new environments in various ways, but the main culprit is human activity.
In some cases, small organisms attach themselves to trade or commercial vessels. Many invasive species of fish enter the Mediterranean Sea via the Suez Canal, a man-made waterway that connects to the Red Sea.
Until 2015, a high salinity area acted as a natural barrier between the two seas. When the canal was widened and deepened, this barrier was removed, allowing invasive species to cross over.
This combined with rising sea temperatures has led to an increase in non-native species in the Mediterranean Sea.